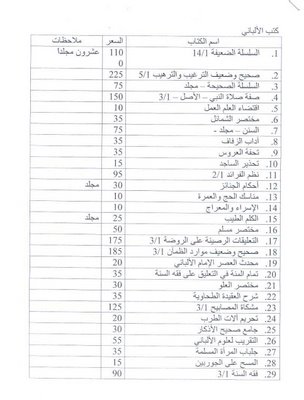
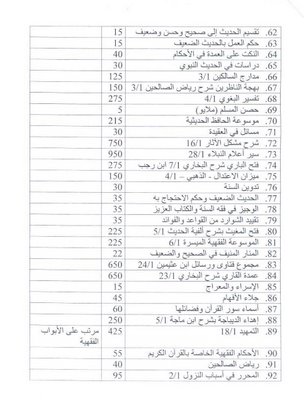
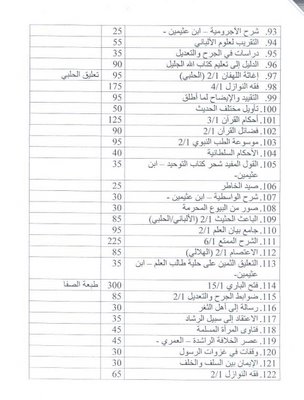
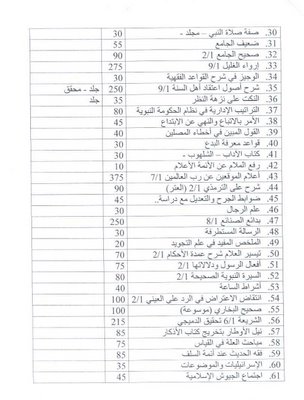
[drp, draft]
Introduction
Housewife as a wife of her husband is required to fulfill several responsibilities. According to Sheikh Abu Bakar Jabir Al-Jazaairy, a woman need to observe daily prayers, obey her husband or her parent if she has no husband, educate her children on beneficial things and teach them good manner, manage household, do good to parent and communicate with them, maintain her dignity and fulfills the rights of the neighbors (1405H). Managing household includes to ensure cleanliness and well-organized of a house. In addition, housewife also needs to take charge of the required nutrition of the family while helping her husband on financial matters through working. As well, she is expected to hinder the household from the unwanted family conflict. Fulfilling the rights of the neighbors includes interacting with them, helping each other and preserving their delight. The most important things that women, including housewife, must know is about believe and religious obligations (Sheikh Abu Bakar Al-Jazaairy, 1405H).
Ridho Baak Najaad states that an effort by a wife to ensure happiness of her husband is rewarded (2001). He further adds that the specialty of wife is the ability to deliver a baby. This uniqueness makes mothers superior in one aspect over fathers. In fact, the prophet sallallahu ‘alaihi wasallam when asked who possess the right of being obeyed, he repeated the answer three times, “your mother”, and then only he said, “your father” (Khaled Abdurrahman Al-Ek, 1990, p218-219).
Beside taking care of nutrition of the family, a house wife is also expected to know a basic health care to ensure first aid on family members can be performed before asking further treatment in a health center. Also, if there is a family member who suffers from diabetes for example, she needs to act as a nurse if not as a doctor.
Financial problems always requires housewife to voluntarily assist the original person-in-charge. Housewife on this reason has exposed themselves on various field of financial acquisition including commerce, service and agriculture. These require them to know how to perform these economic activities in order for them to get more return on their effort. They need to know the way to grow vegetable, how to produce a marketable product and how to advertise the services provided for example. For instance, a group of housewives have run a traditional cake production in Negeri Sembilan (Muafakat Membawa Berkat, n.d.). Women staying at home also can run business through application of information technology through marketing and advertisement (Siti Fatimah Abdul Rahman, 2002).
As a mother, she is responsible to ensure her children to get the appropriate education. Of course in Islam, scholars put emphasized on the true aqidah in which it determine the destiny of individuals. Islam has put emphasized on educating the children with aqidah tawhid since his young age (Khaled Abdurrahman Al-Ek, 2000, p. 109). A mother is expected to keep her children away from bad influence of the evils. Besides, the children need to be schooled in appropriate and affordable school to guarantee a brighter future.
As a wife, it is actually a prescribed way for women to enter the paradise. The way to enter paradise is made different so that individual can act accordingly. Women indeed gain reward through her dressing. Also, jihad which is among the highest ranking of reward, for women is to perform hajj. Besides, women especially housewife is not preferable to out from home for da’wah. As shown by the wives of the prophet who were the most knowledgeable women on Islam. Their state of being in home is the best practice and highly rewarded as they are not permitted to spread Islamic call. Thus, for them is to learn on how they should act accordingly, as a housewife, in order to enter the paradise.
Statement of problem
The aforementioned responsibilities of housewife, if it is performed accordingly, it may bring the family institution to a level which beneficial to the society or at least preserve the peace of the society. A lot of problems such as apostasy, zina, rape, sumbang mahram, drug addiction, gangsterism, political division, prostitution, robbery, suicide, deviant teaching, unemployment, AIDS, terrorism, homicide will at least be reduced, if not totally solved.
Therefore it is a need to study on how housewife acquire the needed information in order for them to well perform their duties. The information needs of them also will be studied together with their information seeking behavior.
Research Questions
This study will try to investigate the information needs and information seeking behavior of housewife. In order to guide the investigation, there are several questions are outlined:
1. What is the information need of housewife?
2. What is their source of information?
3. How is their information seeking behavior?
4. Is there any barrier to information?
5. What is the best solution for the related problems?
Objective of the study
1. to identify their information needs
2. to identify their source of information
3. to investigate their information seeking behavior
4. to assess barrier to information, if any
5. to provide useful recommendation that can assist in designing a better information system for them
Definition of terms
Sungai Cincin
Housewife is the wife of a householder; the mistress of a family; the female head of a household. (Biology-Online.Org, 2006) or a married woman in charge of a household (Merriam-Webster Onine (2006). Regardless of whether they are working or not.
wordnet.princeton.edu/perl/webwn
Information needs
Information seeking behavior
Limitations and delimitations of the study
1. This study will investigate the information needs and information behavior of housewives in a Muslim society of Malaysia. (Limitation by respondents).
2. It will covers only housewives in a village called Kampong Sungai Cincin. (Limitation by geography).
3. It will covers only housewives from Pinggiran Dua, Kampong Sungai Cincin. (Limitation by group).
4. It will consider all level of academic qualification.
(Limitation by qualification).
5. It will cover married, single mother, working and non-working housewife. (Scope of status).
Significance of the study
It is known to the people that housewife is part of family institution. Fine family institution, will lead to a fine society. Being part of family member that constructed society, housewife plays significant role somehow in preserving the peacefulness of a society. This role of course can be successfully performed by housewife given a right quantity and format of information. the use of information is primarily on decision making and to act on something. For instance, best way to communicate with husband or children and best food for family nutrition.
LITERATURE REVIEW
Information is known to be very significant for each aspect of society and to understand the information needs of them is definitely crucial for librarians or service providers in order to provide better service. In fact, according to Alemna and Skouby (2000), information important to legislature as it is needed in decision making process in which may affect the whole nation. Dominic argues that immigrants need information for their self development and their environment (2005). On the other hand, Margaret observes that the lack of information in the right quantity and format is the cause for 70% of rural dwellers in Nigeria live in crusting poverty (2002). Information as well as communication also is important in helping people to cope with cancer (Layden, 2000).
Hence, there are a lot of studies done on various aspects of society related with information. For instance, information needs and information seeking behavior of immigrant (Dominic, 2005; Su and Conaway, 1995; Flythe, 2001; Fisher et al, 2004; etc), Information seeking of Somali women on maternity and health ((Myfanwy M. Davies and Peter A Bath, 2001), information needs and information seeking behavior of rural dwellers (Margaret, 2002), and etc.
However there has been relatively very little empirical research from a library and information science viewpoint on information needs and information seeking behavior of housewives. Generally there are several studies conducted on housewives on various topics such as healthiness (SG Haynes and M Feinleib, 1980), preparation of food (Ralph W. Jackson, Stephen W. McDaniel, C. P. Rao, 1985), dissonance reduction (Jagdish N. Sheth, 1970), reaction on husband retirement (Elizabeth A. Hill, Lorraine T. Dorfman, 1982), politic (Casey, Heather Gollmar, 2000), the role of women in marketing system (Layton, Merrilyn Fay, 2001) strategies of learning to live in foreign country (Inaba, Hisako, 2000), positive stress management (Kim, Jong Hyun, 1997), effect of coffee drinking (Goldstein A, Kaizer S., 1969), agoraphobic (Buglass D, Clarke J, Henderson AS, Kreitman N., 1977).
A number of studies on women on the field of information science is also found such as use of information on antenatal and post natal care by minority ethnic women (Myfanwy M. Davies and Peter A Bath, 2001), information seeking on web by women in IT profession (Chun Wei Choo and Christine Martine, 2003), and etc.
Research methodology of the previous study
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Research design
According to Cresswell, researchers can adopt quantitative, qualitative or combination of both designs for research design. For this study, quantitative design is selected for some reasons.
First of all, the combination of qualitative and quantitative is not suitable for Directed Research Practicum as it is normally used for funded research because it is costly and time-consuming. Also, this study is carried out not by skilled researcher as required by the design.
Researcher also is familiar and comfortable to use survey and experimental instrument rather than being close with the object of the study. Beside that, data collection and analysis processes for this study also need to be accomplished in a shorter time period. Furthermore, the design also promises low risk and ambiguity avoidance for its fixed procedure.
Sample, population and subject
The sample will be housewife from Kampung Sungai Cincin. The subject covers only those who have at least a son or daughter. There are 30 academic scholars will be selected from IIUM (faculty of Islamic studies and law only), which randomly selected. Furthermore, sampling will be used to allow results to be generalized to a well-defined target group. In this study, random sampling will be used to make sure everybody of the population has an equal chance of being selected.
Variables in the study
Instrument and materials
Pre-testing research instrument
Data collection
Data analysis
References
Khaled Abdurrahman Al-Ek (1990). Binaak al-Usrah al-Muslimah. Beirut: Dar Al-Makrifah.
Khaled Abdurrahman Al-Ek (2000). Tarbiyyah Abnaak wa al-Banaat fi Dhauk al-Quran wa al-Sunnah. Beirut: Dar Al-Makrifah.
Siti Fatimah Abdul Rahman (2002). Teknologi Maklumat (TM) Memperkaya Wanita. Retrieved on September 8, 2006 from IKIM website: http://www.ikim.gov.my/bm/artikel/bm.htm#2002
Thursday, September 21, 2006
Grey literature
GREY LITERATURE
By Abdul Latef bin Alhadri
Introduction
There are various types of information sources available online and offline for interested parties. However, it is not necessary for anybody to just browse any sources to look for needed information. Every field has their own major information sources. For instance, students of psychology department may not consult maps for his study while students of geology faculty, consulting a map are a must. Therefore, in serving their clientele, reference librarian must be familiar with the resources as well as to know the background of his clientele.
Grey literature, one type of information sources, is a source that is always consulted by clientele of science and technology background. This source, for them, is considered as a major reference material.
What is grey literature?
Mason stresses that grey literature is highly intellectual and significant for research and development in various subject areas (Mason M.K., 2006, para.1). He also emphasizes that it is a literature that is not attainable through usual channel such as publishers but it is usually original and recent. According to Hargis Library, GL refers to,
“…papers, reports, technical notes or other documents produced and published by governmental agencies, academic institutions and other groups that are not distributed or indexed by commercial publishers. Many of these documents are difficult to locate and obtain (Hargis Library, n.d., grey literature section, para 1).”
In addition, Irwin emphasizes that grey literature refers to publications that issued by government, academia, business, and industry, both in digital and printed formats, and is not controlled by profit interest where publishing is not the primary business activity of the organization (2000, para. 1). Grey literature also is referred to as semi published publication and all non-conventional material that is not obtainable through the conventional, commercial distribution channel (Vilma et al, 1990, p. 358). However, for some countries, there are some agencies that offer distribution of grey literature on request with some fees (Vilma et al, 1990, p. 358).
Many have perceived grey literature as a part of the primary sources of information and it has become an accepted method of non-conventional communication in the sciences and technology (Nancy and William, 2003). It seems like information and communication technology has made it available for almost everybody connected to online. As stressed by Nancy and William, Grey Literature was “grey” and “fugitive” and it has become as importance as journals, books, serials, and specifications because of improvement in term of speed and flexibility of dissemination (2003, p.435). According to Vilma et al, in 1990, all producers and users of grey literature have considered it as an important source but librarian not includes it in their catalog (1990, p. 358).
Attempts to have a uniform definition of Grey Literature have been made several times. In 1997, international conference of Grey Literature has been held in Luxemburg and in 2004, it was held in New York. The conferences defined Grey Literature as:
"Information produced on all levels of government, academics, business and industry in electronic and print formats not controlled by commercial publishing i.e. where publishing is not the primary activity of the producing body." (Grey Literature International Steering Committee (GLISC), 2006, p.1)
Brief history
Grey literature used to be a second over journal articles and books. Its characters as difficult to retrieve, poor in formal quality, produced in limited number of copies and addressed only to small groups or invisible colleges made it less important than others (De Castro P, Salinetti S., 2005, p. 1). However now, it has been considered as a major reference (De Castro P, Salinetti S., 2005, p. 1).
Historically, grey literature was tantamount to report literature (Mason, 2006, para 5). At that time, scientific communication is very important as for research and development (Mason, 2006, para 6). Consequently, World War Two has transformed the literature into a major means of communication (Mason, 2006, para 6). Beside that, development in advance weapon technology requires accurate and speedy communication. Hence, Grey Literature became attractive as the communication needs security and confidential (Mason, 2006, para 6).
By 1970s, most institutions over the world recognized dissertation as an important readings even it is difficult to acquired (Mason, 2006, para 8). In 1978, the term was collectively accepted in York Seminar and confirmation of the vitality of Grey Literature was sought (Vilma et al, 1990, p. 359). As a result, Commission of the European Communities and the British Library Lending Division cooperate to form special database for grey literature called “SIGLE or System for Information on Grey Literature in Europe” (Mason, 2006, para 8 and Vilma et al, 1990, p. 359). As well, with the production and diffusion of a specific standard for technical reports, the ISO 5966/82, application of formal requirement for a correct presentation of Grey Literature has been adopted by issuing organizations (De Castro P, Salinetti S., 2005, p. 1). . This leads to the improvement of quality of documents and their retrieval through bibliographic databases (De Castro P, Salinetti S., 2005, p. 1). Italian Library Association, in 1985, recognized the importance of Grey Literature and European initiative and formed a study group to cater issues about Grey Literature (Vilma et al, 1990, p. 359).
In 1990s, Grey Literature further improved in term of quality and availability, through the wide use of Desk Top Publishing and the internet (De Castro P, Salinetti S., 2005, p. 1). Recently, in 2005, there is a called from specialist to further improve the Grey Literature in term of uniformity (De Castro P, Salinetti S., 2005, p. 2). The uniformity is believed to totally change the physical look of grey literature into black and white literature, in which it is before, distinguishable through its physical attributes (De Castro P, Salinetti S., 2005, p. 5).
What comprise grey literature?
Grey literature comprises materials that are produced by non-commercial entities such as educational centers and universities, research institutes, laboratories, professional societies, government and quasi-government organization (Nancy and William, 2003, p.435). According to Irwin, Grey Literature is produced by government agencies, professional organizations, research centers, universities, public institutions, special interest groups, associations and societies whose main interest is to circulate up to date information to an extensive audience (2000, para 2).
An example given by Irwin, for government agencies is United States Government Printing Office (GPO) who is responsible to publish and circulate information for the whole federal community in various format including printed, microfiche, CD-ROM, and online technology (2000, para 2). Professional organizations published and spread grey literature such as special publications, fact sheets, bulletins and conference proceedings.
Newsletter is one type of grey literature. It is a serial publication consisting of no more than a few pages that contains news, announcements, and current information of interest primarily to a specialized group of subscribers or members of an association or organization who receive it as part of their membership (ODLIS, 2004, section N).
Another type of grey literature is fact sheet which refers to a brief printed handout or publication, sometimes available online, giving basic information about a subject, organization, program, etc. and it stresses on currency (ODLIS, 2004, section F).
Bulletins spread research report of organization to members and subscribers. It is a periodical, usually in the form of a pamphlet, distributed by a government agency, society, or other institution, containing announcements, news, and information of current interest, usually more substantial than a newsletter (ODLIS, 2004, section B).
Society or association may organize conference, congress, symposium or other meeting and then published abstracts or reports of papers presented by participants. This publication is called proceeding and it is also a type of grey literature (ODLIS, 2004, section P).
Taxonomic keys, a grey literature that normally used in botanic sciences, refer to a written method of helping people to identify an unknown plant (Fernald, 1950). He further argues that the key provides a structure for sorting via a great deal of information that enable user to quickly skip over many species that do not resemble the plant. Taxonomy is also a science of classification which divided general principles into classes (ODLIS, 2004, section T).
Survey is a scientific study in which data is collected systematically from a selected group of sources (ODLIS, 2004, section S). Survey also is included in the family of grey resources.
Grey literature also includes report which is a published record of research findings, research still in progress, or other technical findings. It also refers to an official record of the activities of an organization or a group of committee, the proceedings of a government body or an investigation of an agency. It is issued on regular intervals (ODLIS, 2004, section R)
Patent is a legal document issued by an authoritative body to the inventor or originator of a new product or process that granted the exclusive right to manufacture, use, and sell it for a specific period of time (ODLIS, 2004, section P). It is also hard to acquired therefore it is included in grey literature.
A major part of grey literature is translation in which most scientists need it besides dissertations and meeting papers or preprints (Mason, 2006, para 4)
Handbook is a single-volume reference book of compact size that gives concise factual information on a specific subject, systematically organized for quick and easy access (ODLIS, 2004, section H).
Memorandum is an official note circulated internally to one or more persons in a company, society, organization, or institution, with a header indicating the date it was sent and stating to whom it is addressed, from whom it is sent, and the subject of the text (ODLIS, 2004, section M). Memoranda is also perceived as a grey literature as its exclusiveness.
How does grey literature benefit us?
Grey literatures provide students an introduction and overviews for them on their research interest (Irwin, para 4). It also plays a vital role in informing the public and providing the facts that is needed by citizens in order to involve in government and organization that are part of their daily life (Irwin, para 4). Many databases regard grey literature as an essential part of the body of literature for various disciplines as there are some information that cannot be found except in grey literature (Irwin, para 4).
According to a study conducted Velma et al, grey literature was cited mainly in the bibliographies of those journals that provided reliable data on research in progress or mainly deal with scientific developments as influencing regulatory government decisions (Vilma et al, 1990, p. 362).
Irwin states that people consult grey literature to make decision on their daily lives (2000, para 6). For instance, people use repair manual and user manual for home appliances, they also consult tour guide and brochures when they travels and read clinic’s brochure to cure minor illness (Irwin, 2000, para 6).
Conclusion
In short, it is necessary for librarians, especially reference librarians, to have at least basic knowledge on resources that is considered important by the library patrons. This knowledge is important to ensure excellent service that will indirectly contribute to the development of science and technology and other fields.
References
De Castro P and Salinetti S (2005). Uniform Requirements for grey literature: proposal for the adoption of “Nancy style". Seventh International Conference on Grey Literature - Open Access to Grey Resources Nancy, 5-6 December 2005, Round Table: Quality Assessment of Grey Literature.
Fernald, ML (1950). Gray’s Manual of Botany. 8th ed., American Book Company, New York. Retrieved on September 13, 2006 from http://www.bookrags.com/research/taxonomic-keys-plsc-04/
Irwin W (2000). The Role of Grey Literature in Sciences. Retrieved on September 13, 2006 from http://library.brooklyn.cuny.edu/access/falllacc.html).
Mason KM (2006). Grey Literature: its history, definition, acquisition, and cataloguing. Retrieved on September 13, 2006 from MKM website: http://www.moyak.com/researcher/resume/papers/var7mkmkw.html
Nancy L. P and William H. W. (2003). Bibliometric Study of Grey Literature in Core Veterinary Medical Journals. Retrieved on September 13, 2006 from http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pubmed&pubmedid=14566374
Reitz, JM (2004). Online Dictionary for Library and Information Science. Retrieved on September 13, 2006 from http://lu.com/odlis/odlis_n.cfm
Vilma A, De Casto P, and Maria Rossi MA (1990, October). The use of grey literature in health sciences: a preliminary survey. Bulletin of Med Libr Assoc 78(4) October 358-363.
By Abdul Latef bin Alhadri
Introduction
There are various types of information sources available online and offline for interested parties. However, it is not necessary for anybody to just browse any sources to look for needed information. Every field has their own major information sources. For instance, students of psychology department may not consult maps for his study while students of geology faculty, consulting a map are a must. Therefore, in serving their clientele, reference librarian must be familiar with the resources as well as to know the background of his clientele.
Grey literature, one type of information sources, is a source that is always consulted by clientele of science and technology background. This source, for them, is considered as a major reference material.
What is grey literature?
Mason stresses that grey literature is highly intellectual and significant for research and development in various subject areas (Mason M.K., 2006, para.1). He also emphasizes that it is a literature that is not attainable through usual channel such as publishers but it is usually original and recent. According to Hargis Library, GL refers to,
“…papers, reports, technical notes or other documents produced and published by governmental agencies, academic institutions and other groups that are not distributed or indexed by commercial publishers. Many of these documents are difficult to locate and obtain (Hargis Library, n.d., grey literature section, para 1).”
In addition, Irwin emphasizes that grey literature refers to publications that issued by government, academia, business, and industry, both in digital and printed formats, and is not controlled by profit interest where publishing is not the primary business activity of the organization (2000, para. 1). Grey literature also is referred to as semi published publication and all non-conventional material that is not obtainable through the conventional, commercial distribution channel (Vilma et al, 1990, p. 358). However, for some countries, there are some agencies that offer distribution of grey literature on request with some fees (Vilma et al, 1990, p. 358).
Many have perceived grey literature as a part of the primary sources of information and it has become an accepted method of non-conventional communication in the sciences and technology (Nancy and William, 2003). It seems like information and communication technology has made it available for almost everybody connected to online. As stressed by Nancy and William, Grey Literature was “grey” and “fugitive” and it has become as importance as journals, books, serials, and specifications because of improvement in term of speed and flexibility of dissemination (2003, p.435). According to Vilma et al, in 1990, all producers and users of grey literature have considered it as an important source but librarian not includes it in their catalog (1990, p. 358).
Attempts to have a uniform definition of Grey Literature have been made several times. In 1997, international conference of Grey Literature has been held in Luxemburg and in 2004, it was held in New York. The conferences defined Grey Literature as:
"Information produced on all levels of government, academics, business and industry in electronic and print formats not controlled by commercial publishing i.e. where publishing is not the primary activity of the producing body." (Grey Literature International Steering Committee (GLISC), 2006, p.1)
Brief history
Grey literature used to be a second over journal articles and books. Its characters as difficult to retrieve, poor in formal quality, produced in limited number of copies and addressed only to small groups or invisible colleges made it less important than others (De Castro P, Salinetti S., 2005, p. 1). However now, it has been considered as a major reference (De Castro P, Salinetti S., 2005, p. 1).
Historically, grey literature was tantamount to report literature (Mason, 2006, para 5). At that time, scientific communication is very important as for research and development (Mason, 2006, para 6). Consequently, World War Two has transformed the literature into a major means of communication (Mason, 2006, para 6). Beside that, development in advance weapon technology requires accurate and speedy communication. Hence, Grey Literature became attractive as the communication needs security and confidential (Mason, 2006, para 6).
By 1970s, most institutions over the world recognized dissertation as an important readings even it is difficult to acquired (Mason, 2006, para 8). In 1978, the term was collectively accepted in York Seminar and confirmation of the vitality of Grey Literature was sought (Vilma et al, 1990, p. 359). As a result, Commission of the European Communities and the British Library Lending Division cooperate to form special database for grey literature called “SIGLE or System for Information on Grey Literature in Europe” (Mason, 2006, para 8 and Vilma et al, 1990, p. 359). As well, with the production and diffusion of a specific standard for technical reports, the ISO 5966/82, application of formal requirement for a correct presentation of Grey Literature has been adopted by issuing organizations (De Castro P, Salinetti S., 2005, p. 1). . This leads to the improvement of quality of documents and their retrieval through bibliographic databases (De Castro P, Salinetti S., 2005, p. 1). Italian Library Association, in 1985, recognized the importance of Grey Literature and European initiative and formed a study group to cater issues about Grey Literature (Vilma et al, 1990, p. 359).
In 1990s, Grey Literature further improved in term of quality and availability, through the wide use of Desk Top Publishing and the internet (De Castro P, Salinetti S., 2005, p. 1). Recently, in 2005, there is a called from specialist to further improve the Grey Literature in term of uniformity (De Castro P, Salinetti S., 2005, p. 2). The uniformity is believed to totally change the physical look of grey literature into black and white literature, in which it is before, distinguishable through its physical attributes (De Castro P, Salinetti S., 2005, p. 5).
What comprise grey literature?
Grey literature comprises materials that are produced by non-commercial entities such as educational centers and universities, research institutes, laboratories, professional societies, government and quasi-government organization (Nancy and William, 2003, p.435). According to Irwin, Grey Literature is produced by government agencies, professional organizations, research centers, universities, public institutions, special interest groups, associations and societies whose main interest is to circulate up to date information to an extensive audience (2000, para 2).
An example given by Irwin, for government agencies is United States Government Printing Office (GPO) who is responsible to publish and circulate information for the whole federal community in various format including printed, microfiche, CD-ROM, and online technology (2000, para 2). Professional organizations published and spread grey literature such as special publications, fact sheets, bulletins and conference proceedings.
Newsletter is one type of grey literature. It is a serial publication consisting of no more than a few pages that contains news, announcements, and current information of interest primarily to a specialized group of subscribers or members of an association or organization who receive it as part of their membership (ODLIS, 2004, section N).
Another type of grey literature is fact sheet which refers to a brief printed handout or publication, sometimes available online, giving basic information about a subject, organization, program, etc. and it stresses on currency (ODLIS, 2004, section F).
Bulletins spread research report of organization to members and subscribers. It is a periodical, usually in the form of a pamphlet, distributed by a government agency, society, or other institution, containing announcements, news, and information of current interest, usually more substantial than a newsletter (ODLIS, 2004, section B).
Society or association may organize conference, congress, symposium or other meeting and then published abstracts or reports of papers presented by participants. This publication is called proceeding and it is also a type of grey literature (ODLIS, 2004, section P).
Taxonomic keys, a grey literature that normally used in botanic sciences, refer to a written method of helping people to identify an unknown plant (Fernald, 1950). He further argues that the key provides a structure for sorting via a great deal of information that enable user to quickly skip over many species that do not resemble the plant. Taxonomy is also a science of classification which divided general principles into classes (ODLIS, 2004, section T).
Survey is a scientific study in which data is collected systematically from a selected group of sources (ODLIS, 2004, section S). Survey also is included in the family of grey resources.
Grey literature also includes report which is a published record of research findings, research still in progress, or other technical findings. It also refers to an official record of the activities of an organization or a group of committee, the proceedings of a government body or an investigation of an agency. It is issued on regular intervals (ODLIS, 2004, section R)
Patent is a legal document issued by an authoritative body to the inventor or originator of a new product or process that granted the exclusive right to manufacture, use, and sell it for a specific period of time (ODLIS, 2004, section P). It is also hard to acquired therefore it is included in grey literature.
A major part of grey literature is translation in which most scientists need it besides dissertations and meeting papers or preprints (Mason, 2006, para 4)
Handbook is a single-volume reference book of compact size that gives concise factual information on a specific subject, systematically organized for quick and easy access (ODLIS, 2004, section H).
Memorandum is an official note circulated internally to one or more persons in a company, society, organization, or institution, with a header indicating the date it was sent and stating to whom it is addressed, from whom it is sent, and the subject of the text (ODLIS, 2004, section M). Memoranda is also perceived as a grey literature as its exclusiveness.
How does grey literature benefit us?
Grey literatures provide students an introduction and overviews for them on their research interest (Irwin, para 4). It also plays a vital role in informing the public and providing the facts that is needed by citizens in order to involve in government and organization that are part of their daily life (Irwin, para 4). Many databases regard grey literature as an essential part of the body of literature for various disciplines as there are some information that cannot be found except in grey literature (Irwin, para 4).
According to a study conducted Velma et al, grey literature was cited mainly in the bibliographies of those journals that provided reliable data on research in progress or mainly deal with scientific developments as influencing regulatory government decisions (Vilma et al, 1990, p. 362).
Irwin states that people consult grey literature to make decision on their daily lives (2000, para 6). For instance, people use repair manual and user manual for home appliances, they also consult tour guide and brochures when they travels and read clinic’s brochure to cure minor illness (Irwin, 2000, para 6).
Conclusion
In short, it is necessary for librarians, especially reference librarians, to have at least basic knowledge on resources that is considered important by the library patrons. This knowledge is important to ensure excellent service that will indirectly contribute to the development of science and technology and other fields.
References
De Castro P and Salinetti S (2005). Uniform Requirements for grey literature: proposal for the adoption of “Nancy style". Seventh International Conference on Grey Literature - Open Access to Grey Resources Nancy, 5-6 December 2005, Round Table: Quality Assessment of Grey Literature.
Fernald, ML (1950). Gray’s Manual of Botany. 8th ed., American Book Company, New York. Retrieved on September 13, 2006 from http://www.bookrags.com/research/taxonomic-keys-plsc-04/
Irwin W (2000). The Role of Grey Literature in Sciences. Retrieved on September 13, 2006 from http://library.brooklyn.cuny.edu/access/falllacc.html).
Mason KM (2006). Grey Literature: its history, definition, acquisition, and cataloguing. Retrieved on September 13, 2006 from MKM website: http://www.moyak.com/researcher/resume/papers/var7mkmkw.html
Nancy L. P and William H. W. (2003). Bibliometric Study of Grey Literature in Core Veterinary Medical Journals. Retrieved on September 13, 2006 from http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pubmed&pubmedid=14566374
Reitz, JM (2004). Online Dictionary for Library and Information Science. Retrieved on September 13, 2006 from http://lu.com/odlis/odlis_n.cfm
Vilma A, De Casto P, and Maria Rossi MA (1990, October). The use of grey literature in health sciences: a preliminary survey. Bulletin of Med Libr Assoc 78(4) October 358-363.
Friday, September 15, 2006
depository library
depository library
A library legally designated to receive without charge all or a portion of the government documents provided by the U.S. Government Printing Office (GPO) and other federal agencies to the Superintendent of Documents for distribution through the Federal Depository Library Program (FDLP), having made a legal commitment to comply with federal regulations concerning maintenance and accessibility. Some federal depositories also collect publications issued by state government agencies. A regional depository library receives and retains permanently at least one copy of all the documents distributed through the FDLP, but a selective depository library receives only a percentage of the available publications and is required to retain them for a minimum of 5 years. Depository libraries are required to complete a self-study and/or undergo inspection at intervals of 6-7 years to assure compliance with FDLP rules and regulations. Click here to connect to the GPO Access Federal Depository Library locator service. Compare with repository. See also: basic collection, Depository Library Council, and depository library number.
Depository Library Council (DLC)
Formally established in 1972, the Depository Library Council is appointed by the Public Printer to advise on matters pertaining to the Federal Depository Library Program (FDLP) as provided in Title 44 U.S.C. The mission of the DLC is to assist the U.S. Government Printing Office (GPO) in identifying and evaluating alternatives for improving public access to government information through the FDLP and for optimizing available resources. Its 15 members are selected to provide a diverse range of opinion and expertise, and to represent a cross section of the various types of DLP libraries, with at least half of the members employed in depository libraries in positions that provide experience in a documents department. Click here to learn more about the DLC.
see: http://lu.com/odlis/odlis_d.cfm#depository
A library legally designated to receive without charge all or a portion of the government documents provided by the U.S. Government Printing Office (GPO) and other federal agencies to the Superintendent of Documents for distribution through the Federal Depository Library Program (FDLP), having made a legal commitment to comply with federal regulations concerning maintenance and accessibility. Some federal depositories also collect publications issued by state government agencies. A regional depository library receives and retains permanently at least one copy of all the documents distributed through the FDLP, but a selective depository library receives only a percentage of the available publications and is required to retain them for a minimum of 5 years. Depository libraries are required to complete a self-study and/or undergo inspection at intervals of 6-7 years to assure compliance with FDLP rules and regulations. Click here to connect to the GPO Access Federal Depository Library locator service. Compare with repository. See also: basic collection, Depository Library Council, and depository library number.
Depository Library Council (DLC)
Formally established in 1972, the Depository Library Council is appointed by the Public Printer to advise on matters pertaining to the Federal Depository Library Program (FDLP) as provided in Title 44 U.S.C. The mission of the DLC is to assist the U.S. Government Printing Office (GPO) in identifying and evaluating alternatives for improving public access to government information through the FDLP and for optimizing available resources. Its 15 members are selected to provide a diverse range of opinion and expertise, and to represent a cross section of the various types of DLP libraries, with at least half of the members employed in depository libraries in positions that provide experience in a documents department. Click here to learn more about the DLC.
see: http://lu.com/odlis/odlis_d.cfm#depository
depository library
A library legally designated to receive without charge all or a portion of the government documents provided by the U.S. Government Printing Office (GPO) and other federal agencies to the Superintendent of Documents for distribution through the Federal Depository Library Program (FDLP), having made a legal commitment to comply with federal regulations concerning maintenance and accessibility. Some federal depositories also collect publications issued by state government agencies. A regional depository library receives and retains permanently at least one copy of all the documents distributed through the FDLP, but a selective depository library receives only a percentage of the available publications and is required to retain them for a minimum of 5 years. Depository libraries are required to complete a self-study and/or undergo inspection at intervals of 6-7 years to assure compliance with FDLP rules and regulations. Click here to connect to the GPO Access Federal Depository Library locator service. Compare with repository. See also: basic collection, Depository Library Council, and depository library number.
Depository Library Council (DLC)
Formally established in 1972, the Depository Library Council is appointed by the Public Printer to advise on matters pertaining to the Federal Depository Library Program (FDLP) as provided in Title 44 U.S.C. The mission of the DLC is to assist the U.S. Government Printing Office (GPO) in identifying and evaluating alternatives for improving public access to government information through the FDLP and for optimizing available resources. Its 15 members are selected to provide a diverse range of opinion and expertise, and to represent a cross section of the various types of DLP libraries, with at least half of the members employed in depository libraries in positions that provide experience in a documents department. Click here to learn more about the DLC.
see: http://lu.com/odlis/odlis_d.cfm#depository
A library legally designated to receive without charge all or a portion of the government documents provided by the U.S. Government Printing Office (GPO) and other federal agencies to the Superintendent of Documents for distribution through the Federal Depository Library Program (FDLP), having made a legal commitment to comply with federal regulations concerning maintenance and accessibility. Some federal depositories also collect publications issued by state government agencies. A regional depository library receives and retains permanently at least one copy of all the documents distributed through the FDLP, but a selective depository library receives only a percentage of the available publications and is required to retain them for a minimum of 5 years. Depository libraries are required to complete a self-study and/or undergo inspection at intervals of 6-7 years to assure compliance with FDLP rules and regulations. Click here to connect to the GPO Access Federal Depository Library locator service. Compare with repository. See also: basic collection, Depository Library Council, and depository library number.
Depository Library Council (DLC)
Formally established in 1972, the Depository Library Council is appointed by the Public Printer to advise on matters pertaining to the Federal Depository Library Program (FDLP) as provided in Title 44 U.S.C. The mission of the DLC is to assist the U.S. Government Printing Office (GPO) in identifying and evaluating alternatives for improving public access to government information through the FDLP and for optimizing available resources. Its 15 members are selected to provide a diverse range of opinion and expertise, and to represent a cross section of the various types of DLP libraries, with at least half of the members employed in depository libraries in positions that provide experience in a documents department. Click here to learn more about the DLC.
see: http://lu.com/odlis/odlis_d.cfm#depository
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)